
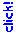
NRL GOES E/W Composite VIS/IR (Day/Night)
Post-tropical remnant low Dolores is west of Baja
Saturday, July 18, 2015 5:00 PM PDT.
Downtown Los Angeles (USC) ended the 2014-2015 rainfall year (July 1 - June 30) with 8.52 inches of rain; well below the normal of 14.93 inches. It was the fourth consecutive year of below normal rainfall in Los Angeles and much of Southern California.
To kick off the new new rainfall year two waves of moisture and instability associated with ex-hurricane Dolores, other tropical sources, and a strong monsoonal flow from Baja resulted in record-setting rainfall in Southern California from Saturday July 18 to Monday July 20.
Constructive interference of the El Nino base state by the active phase of the MJO resulted in negative 200-hPa velocity potential anomalies and enhanced convection in the Eastern Pacific during the first half of July. This appears to have contributed to the rapid development of Dolores from a tropical depression on July 11 into a Category 4 hurricane July 15. Anomalously warm SSTs in the tropical and sub-tropical Eastern Pacific also played a role, helping to maintain the strength of Dolores and increasing the amount of water vapor entrained by the system and transported into Southern California.
Many stations set new records, not only for the date, but for any day in July. Downtown Los Angeles (USC) set rainfall records for the date on Saturday and Sunday and tied Monday's record. Downtown Los Angeles recorded 0.36 inch of rain Saturday. This is more rain than any day in any July since recordkeeping began in 1877. That one day of rainfall even broke the monthly record for July in Los Angeles! Prior to this event the wettest July on record was in 1886, when 0.24 inch was recorded.
There was very heavy rain in the mountains on Sunday, with rain rates exceeding an inch a hour. From 5:15 p.m. to 5:25 p.m. a CBS Radio weather station on Mt. Wilson recorded a half-inch of rain in just 10 minutes!
Though the rain created its own problems -- including flash floods, debris flows and rock slides -- the soaking rains helped quell the Pines Fire near Wrightwood and the North Fire near Cajon Pass. Over the three day period from Saturday to Monday the Big Pines Remote Automated Weather Station (RAWS), near the Pines Fire, recorded 3.12 inches of rain. Several stations in the San Gabriels recorded more than three inches of rain, including Clear Creek and Opids Camp. Here's a NWS compilation of some rainfall totals in the Los Angeles forecast area and the San Diego forecast area.
After dawdling around for several months our on again, off again El Nino is finally firing on all cyclinders and could reach ONI and MEI levels not seen since 1997-98 and 1982-83. The Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI) for May-June was 2.06. This was the third highest value for the season, exceeded only in 1983 (2.2) and 1997 (2.3). It is the second highest for the season during the development phase of an El Nino event. The 2015 April-May-June Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) value of 0.9 was higher than than in 1982 (0.6) and 1997 (0.6). Several dynamical models in the IRI/CPC ENSO Predictions Plume of forecast Nino 3.4 SST anomaly, released July 16, project Nino 3.4 SST anomalies in excess of 2.5°C this fall.
Analysis of correlations of CMAP Precipitation with globally integrated atmospheric angular momentum using ESRL/PSD's Linear Correlations in Atmospheric Seasonal/Monthly Averages tool suggests that precipitation in the southern half of California is more strongly correlated with atmospheric angular momentum (AAM) than with Nino 3.4 SST. For example, compare the correlation of CMAP Precipitation to AAM and to Nino 3.4 SST for Dec-Jan-Feb 1980-2012. Cyclical increases in relative atmospheric angular momentum are often associated with El Ninos. This can be seen in the plots of the Global Wind Oscillation in my El Nino Comparison Chart.
After being negative for 3 1/2 years, the PDO Index has been positive since January 2014. December's PDO value of 2.51 was the highest for that month on record since 1900. June's value of 1.54 was the 13th highest since 1900.
More information about Southern California weather and climate can be found using our WEATHER LINKS page.