
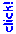
HPC 5-Day Precipitation Forecast
Issued Friday Afternoon, January 20, 2012
Last Sunday's upper level low resulted in a little rain, mostly south of the L.A. basin, but Southern California and much of the West has been dry, dry, dry. How dry? Take a look at this plot of percent of average precipitation for the past 90 days from the Western Regional Climate Center.
Downtown Los Angeles (USC) has not recorded measurable rain for more than a month. The last measurable rain was on December 17 when 0.01 inch recorded. The water year precipitation total for Los Angeles has been stuck on 3.76 inches, which is about 2.5 inches below normal. The Sierra has been especially dry. The Statewide Summary of Snow Water Content for January 18 reported the snowpack at 10% of normal. Remarkably, Mammoth Mountain recorded no natural snow between December 5 and January 19!
The good news is the very stubborn West Coast ridge has finally relented, opening the door to a more zonal flow and a sequence of shortwave troughs. The change in pattern is forecast to produce significant rain and snow over most of the West Coast the next few days. The HPC 5-day Precipitation Forecast indicates up to about 5 inches of precipitation in some areas of the Sierra and North Coast, and over 9 inches in some areas of the Pacific Northwest.
The change in pattern isn't forecast to produce much rain south of Pt. Conception, but at this point just about any amount would be helpful. BUFKIT analysis of WRF Ensemble forecasts for Van Nuys indicate precipitation amounts ranging from about 0.1 inch to 0.5 inch, beginning sometime this evening and ending midday Saturday. The 18z NAM precipitation forecast for Van Nuys projects about 0.25 inch for the storm. Some mountain areas could see somewhat higher precipitation totals, particularly those with a west-facing aspect.
Another shortwave is forecast to move through the area Monday. Model projections differ, but we could get a little rain out of that system as well. We'll see!
Update January 25, 2012 8:00 am PST. Precipitation totals across the area from Monday's system generally ranged from about 0.3 inch to 0.75 inch. Downtown Los Angeles (USC) recorded 0.62 inches for the storm. This combined with the 0.68 inches from Saturday's system boosted the water year total for Los Angles to 5.06 inches, which is about 75% of normal for the date. The medium range models have been all over the place. Yesterday the 12z GFS forecast for Monday morning depicted an upper low and trough on the West Coast, while the ECMWF indicated some ridging. Here's a GFS/ECMWF comparison from San Jose State University Meteorology. Given the recent Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) and rejuvenation of the MJO there's plenty of uncertainty in the medium range. The ECMWF seems to like the idea of a relatively fast-moving trough affecting the West Coast sometime around February 1. We'll see!
Update January 21, 2012 1:30 pm PST. Perhaps because its jet stream dynamics were more favorable than expected, this first system was a little stronger and held together a little better south of Pt. Conception than suggested by the models. Rainfall totals tabulated by the NWS generally ranged from about 0.2 to 0.7 inch in the Los Angeles area, with somewhat higher totals recorded in Ventura County and Santa Barbara County. Model projections have varied on the strength of the system forecast to move through the area on Monday. The 12z NAM projected about 0.4 inch for Van Nuys; the 18z NAM about 0.3 inch, and the 12z GFS about 0.5 inch. The system appears similar to today's, but it looks like the shortwave trough and vortex max may track more directly into Southern California.
More information about Southern California weather and climate can be found using our WEATHER LINKS page.